Primary vibration sources
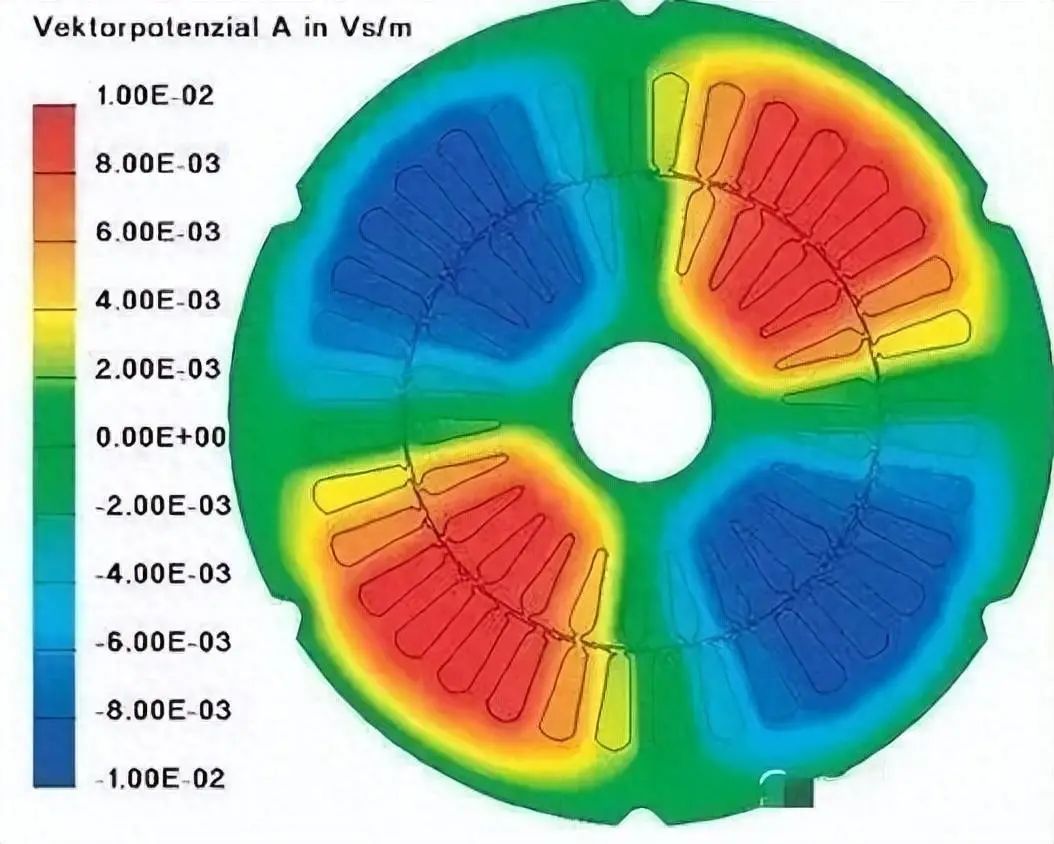
The vibration of permanent magnet synchronous motors has three primary origins: aerodynamic noise, mechanical vibration, and electromagnetic vibration. Aerodynamic noise results from rapid pressure changes inside the motor and friction between the gas and structural surfaces. Mechanical vibration is caused by periodic elastic deformation of bearings, geometric defects, and rotor shaft imbalance. Electromagnetic vibration is driven by electromagnetic excitation: the air-gap magnetic field acting on the stator core induces radial deformation of the stator, transmits to the motor housing, and radiates noise. Although the tangential component of the air-gap magnetic field is small, it can induce cogging torque ripple and contribute to motor vibration. In propulsion applications of permanent magnet synchronous motors, electromagnetic excitation is typically the dominant vibration source.
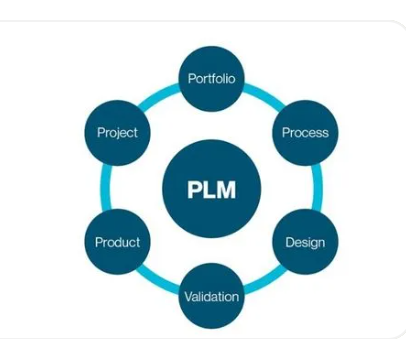
Early-stage design and modeling
As permanent magnet synchronous motors become increasingly vital in sophisticated Industrial Control systems, their early-stage design and modeling have gained significant importance. During the early design stage of permanent magnet synchronous motors, establishing a vibration response model, analyzing the nature of electromagnetic excitation and the dynamic properties of the structure, and predicting and assessing vibration and noise levels enable targeted design optimization. Such an approach can reduce vibration and noise, improve motor performance, and shorten development time.
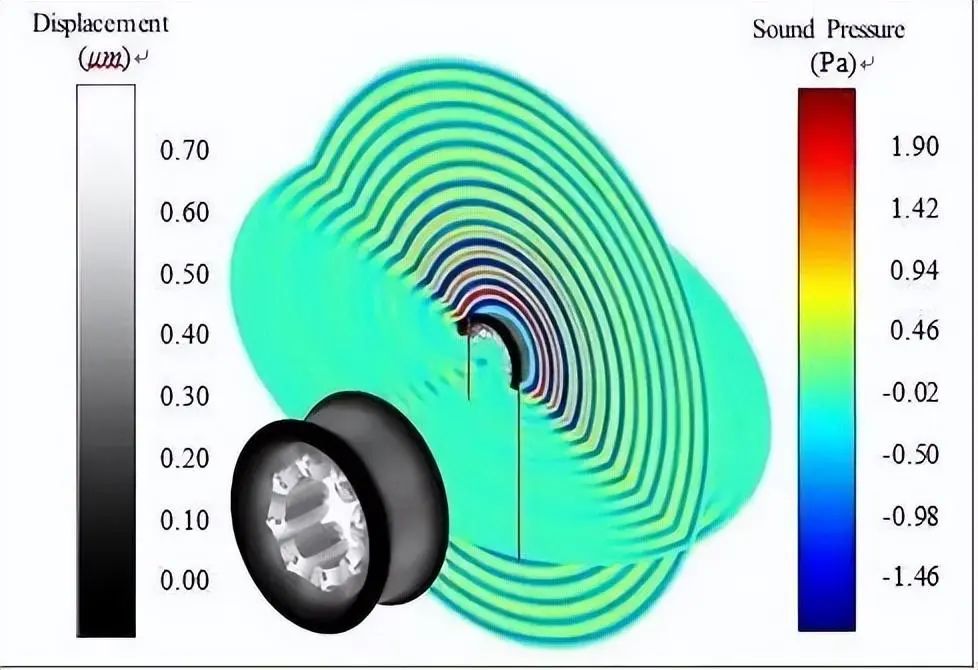
Recent research advances
Current research progress can be summarized in three areas:
1. Electromagnetic excitation
Electromagnetic excitation is the fundamental cause of vibration and has been studied for many years. Early work included calculations of electromagnetic force distributions inside the motor and analytical derivations of radial forces. In recent years, finite element simulation methods and numerical analysis have been widely applied; Chinese and international researchers have studied the effects of different pole-slot configurations on cogging torque of permanent magnet synchronous motors.
2. Structural modal characteristics
Structural modal characteristics are closely related to vibration response, particularly when the excitation frequency is close to a structure's natural frequency, which can lead to resonance. Researchers have used experiments and simulation to study the structural characteristics of the stator system, including factors that influence modal frequencies such as material properties, elastic modulus, and structural parameters.
3. Vibration response under electromagnetic excitation
The vibration response of the motor arises from electromagnetic excitation acting on the stator teeth. Researchers have analyzed the spatio-temporal distribution of electromagnetic forces and applied the resulting excitation to the stator structure to obtain numerical and experimental vibration responses. Studies have also examined how the damping coefficient of the housing material affects vibration response.